Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Sexual Reproduction, Juvenile Phase of Organisms, Vegetative Phase of Organisms, Reproductive Phase of organisms, Senescent Phases of Organisms, Oestrus Cycle, Events in Sexual Reproduction, etc.
Important Questions on Sexual Reproduction
Which of the following statements is true?
The development of embryo in both monocotyledons and dicotyledons
Zygote divides after the formation of endosperm
The following are oviparous except
Select the total number of true statements.
(A) In organisms belonging to fungi and algae, the zygote develops a thick wall that is resistant to dessication and damage.
(B) Formation of diploid zygote is universal in all sexually reproducing organisms.
(C) Syngamy occurs inside the body of the organism in internal fertilization.
(D) In organism with haplontic life cycle, the zygote divides by meiosis to form haploid spores that grow into haploid individuals.
The formation of embryo without fertilisation is called
Read the following statements and select the wrong ones:
I. Juvenile phase is the pre-reproductive phase in the life cycle of an organism.
II. Bamboo species flower only once in their lifetime.
III. Mammals are called continuous breeders.
IV. In the oestrous cycle, broken endometrium is passed out.
Development of new organism without fertilization of female gamete is called
Organisms showing internal fertilisation shows reduction in number of --------gamete and increase in number of ---------gamete.
What is the carrier of 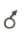 gamete in the Pinus, Marchantia, Mango, Chara, and Funaria respectively?
gamete in the Pinus, Marchantia, Mango, Chara, and Funaria respectively?
[where Pollen tube, ]
Choose the correct option from the following, statements.
I. During embryogenesis, the zygote undergoes mitotic cell division.
II. In organisms with a diplontic life cycle, the zygote divides by meiotic cell division.
III. The pericarp (fruit wall) develops from the integument of the ovule, after fertilization.
IV. In brinjal, sepals remained attached to fruit even after fertilization.
The vital link that ensures continuity of species between organisms of one generation and next are all, except
Which of the following represents the correct sequence of phases in the life cycle of wheat? [where Juvenile phase, Reproductive phase,
Interflowering period, Gap phase,
Senescence, Vegetative phase]
Synchrony between the maturity of sexes and release of many gametes is shown by:
Choose correct option w.r.t. features of different plant groups.
Which of the following features cannot be shown by structure which is vital link between two generations ensuring continuity of species?
(a) Thick walled
(b) Multicelled
(c) One set of chromosomes
(d) Meiocyte
(e) Resting structure
Which of the following plant groups shows internal fertilisation only?
(a) Algae
(b) Bryophytes
(c) Pteridophytes
(d) Fungi
In few fungi and most of the algae:
